Exercise 9.15 An harmonic oscillator with all pass sections?
Given is the circuit below; this circuit is intended to be an harmonic oscillator.
- The opamps are ideal, with a real valued voltage gain
and with no frequency dependency.
- The value of all resistors is the same ().
All capacitors have identical values ().
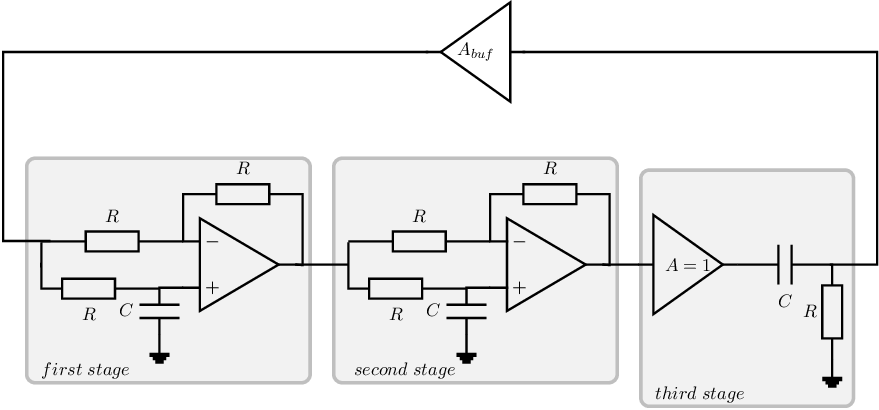
-
(a)
- Which condition(s) must be satisfied to get harmonic oscillation?
The circuit can be decomposed into 3 stages that have frequency dependent transfer functions
(identified by their gray background in the figure), and one ideal voltage buffer stage with a real
valued voltage gain .
-
(b)
- Show (with a derivation) that the voltage transfer for both the first stage and for the second stage
is .
-
(c)
- Derive the phase shift of each of the three stages for
and for (rad/s).
Note that your answer consists of six phases, two per stage.
-
(d)
- Draw in one Bode plot (magnitude and phase) the voltage transfer of each of the three stages.
You may assume (for this plot)
and .
-
(e)
- Determine whether the given circuit can function as harmonic oscillator using a positive .
If your answer shows that harmonic oscillation can be possible, derive an expression for the
(radian) oscillation frequency and for the required .
Otherwise demonstrate clearly (mathematically) that this circuit cannot oscillate harmonically.
Explicit hint: using the findings in the previous 2 questions or using standard forms for transfer
functions simplifies significantly.
-
(f)
- Determine whether the given circuit can function as harmonic oscillator using a negative .
If your answer shows that harmonic oscillation can be possible, derive an expression for the
(radian) oscillation frequency and for the required .
Otherwise demonstrate clearly (mathematically) that this circuit cannot oscillate harmonically.
Explicit hint, the same one: using the findings in the previous 2 questions or using standard
forms for transfer functions simplifies significantly.

